TRANSLATE trial: LATP vs TRUS Bx
- Jul 1, 2025
- 2 min read
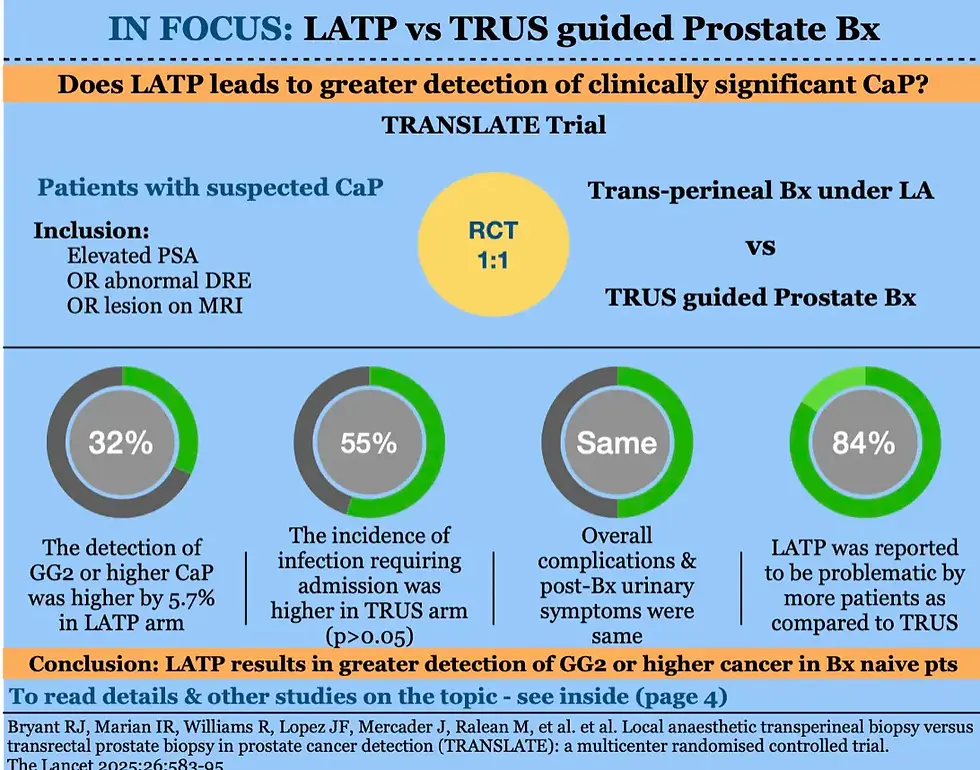
The TRANSLATE trial was a multi-centre RCT performed at 10 centres in the UK.( 1 ) Biopsy naive patients with suspected CaP were randomised to either transperineal Bx under local anaesthesia or TRUS guided prostate biopsy. A total of 1126 pts were randomised and the follow up was upto 4 months post-biopsy. No antibiotics were prescribed to LATP arm whereas the TRUS arm received standard antibiotics & augmented or culture directed antibiotics were not prescribed. Also, authors mandated that 12 systematic cores were taken in both the arms along with 3-4 targeted cores to ensure equal number of cores taken in both the arms. The primary objective of the study was to compare the detection of GG2 or higher CaP, whereas, infectious complications, overall complications, post biopsy urinary and sexual function and the procedure related discomfort constituted the secondary outcomes. 562 pts were assigned to LATP and 562 were assigned to TRUS Bx. The detection of GG2 or higher CaP was greater in LATP arm by 5.7% (60.1% vs 54.4%,OR 1.32, p=0.031). However, the detection of any-grade cancer and detection of GG 3-5 were similar between the two groups. The infection rate at 4 months, requiring hospitalisation, was higher in TRUS arm (<1% vs 2%) however, it did not reach statistical significance. The overall infection rate, with or without hospitalisation, was similar between the two arms (20% vs 21%).
The overall complication rate, including urinary retention, hematuria, blood in faces, pain etc, were also similar. The post biopsy urinary symptoms on IPSS and sexual function on IIEF were also similar in the two arms. However, a larger percentage of patients reported LATP to be problematic procedure (38% vs 27%). The scores for procedure related pain, discomfort and embarrassment were higher in the LATP arm. A total of 4 RCTs have been reported on this topic and all have provided mixed results (PERFECT, PROBE-PC, PREVENT). The detection of cancer and infectious complications are the usual points of contention and all RCTs have reported varied results, with some reporting higher CaP detection in TP biopsy whereas, other reporting a similar detection. The rate of infectious complication, the major reason behind shifting to TP Bx, has however, found to be consistently similar in all RCTs. A systematic review of available data is awaited to shed more light on the debate.



Comments